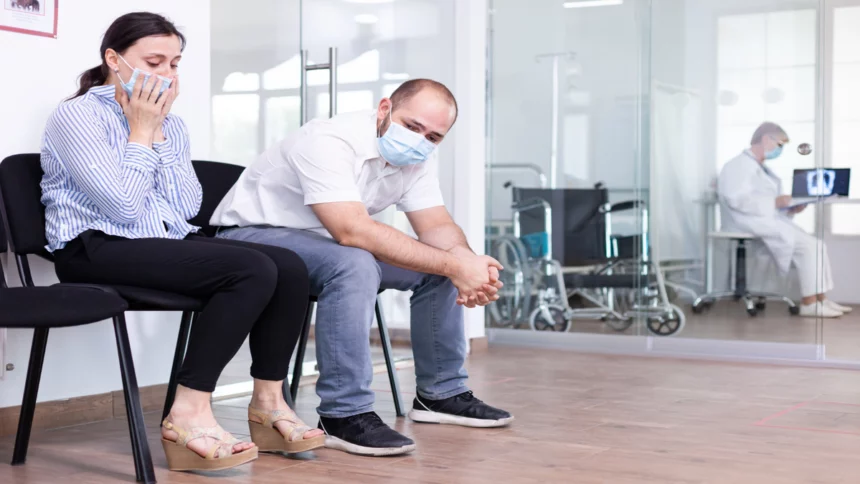
It is undeniable that we live in an increasingly sedentary world. We spend much of our lives sitting at desks, in cars, and on couches, and this lack of physical activity has been linked to a wide range of health problems. Prolonged sitting has been associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, certain cancers, musculoskeletal issues, and mental health problems.
How Sitting Affects Your Health
Prolonged sitting is becoming increasingly prevalent, yet it can have serious health implications. The sedentary lifestyle associated with sitting for extended periods can lead to various health hazards, from increased risk of chronic diseases to muscular problems. How sitting affects your health depends on the length and frequency of the sitting and the posture adopted when sitting. When sitting for long periods, the body’s muscles are not being used, leading to weak and tight muscles. Furthermore, circulation is restricted, causing the body to be deprived of oxygen and other essential nutrients. This can lead to an increased risk of stroke, heart disease, and type 2 diabetes.
Additionally, sitting for long periods can cause a decrease in the production of hormones responsible for burning fat, leading to weight gain. The poor posture adopted when sitting can also cause lower back pain, neck and shoulder pain and headaches. Frequent breaks from sitting and moving around for a few minutes are essential. Doing so can help keep the body active, reduce the health hazards associated with prolonged sitting, and improve health.
Specific Health Risks Associated With Sitting
Specific Health Risks Associated With Sitting: Sitting for long periods has been linked to several health issues, such as obesity, heart disease, diabetes, and back pain. Prolonged sitting can also increase your risk of developing certain types of cancer, such as colon and endometrial cancer. Additionally, sitting for long periods can lead to poor posture, weak abdominal muscles, and poor circulation. Poor posture can lead to neck and shoulder pain, headaches, and carpal tunnel syndrome.
Weak abdominal muscles can result in poor balance and a greater risk of injury. Poor circulation can lead to a decrease in energy and concentration, as well as an increased risk of blood clots. Furthermore, sitting for extended periods can cause the body to produce higher levels of cortisol, the stress hormone. This can lead to a weakened immune system, fatigue, and depression.
The Negative Impact of Prolonged Sitting on Muscles and Bones
Prolonged sitting has been proven to have many health hazards that can affect our muscles and bones. Studies have shown that when we sit for more than two hours, our muscles weaken, and the risk of developing chronic musculoskeletal pain increases. This can lead to decreased physical activity, further exacerbating the problem. In addition, prolonged sitting can increase bone density, leading to an increased risk of osteoporosis. This can lead to an increased risk of bone fractures. Sitting for too long can also lead to poor posture, which can strain the spine and other muscles in the body. This can lead to long-term back pain and other spinal issues. It is important to take regular breaks from sitting and to move around to help reduce the negative impact of prolonged sitting on our muscles and bones.
Effects on the Spine
Prolonged sitting directly impacts the health and functioning of the spine. This is because of the lack of movement and the spine’s position when sitting for long periods. Sitting for hours on end can cause the spine to become compressed and can lead to an increased risk of developing lower back pain. Additionally, prolonged sitting can cause the spine to lose its natural curvature, leading to decreased flexibility and a decreased range of motion. This can also lead to a decrease in posture and overall health. The spine is also responsible for proper circulation, so if sitting for long periods, the spine can become stiff and prevent adequate circulation. This can lead to fatigue, swelling, and even muscle strain.
Mental Health Hazards
The mental health hazards of prolonged sitting can be just as serious as the physical ones. Studies have linked extended periods of sitting to increased depression and anxiety, a lack of focus and concentration, and even a decreased sense of self-worth. Sitting for long periods can lead to a decrease in physical activity, which can, in turn, increase stress and anxiety. This can be compounded by the feeling that you’re not “accomplishing” anything while sitting, which can further negatively affect your mental health.
Additionally, prolonged sitting can lead to decreased energy levels, leading to decreased motivation and productivity. Finally, it can lead to an increase in unhealthy habits, such as over-eating, which can further contribute to depression and anxiety. Taking breaks from sitting and getting up and moving throughout the day is important to help maintain your mental and physical health.
How to Reduce the Negative Effects of Sitting
Prolonged sitting is a serious health hazard that can negatively affect your body long-term. Sitting for extended periods can lead to various health issues, including an increased risk of heart disease, obesity, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Fortunately, there are ways to reduce the negative effects of sitting.
Taking regular breaks to stand or walk around, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining proper posture while sitting can all help to reduce the risks associated with prolonged sitting. Adding a standing desk or adjustable workstation to your home or office can also help reduce the health risks of sitting for long periods. Choosing a chair that supports your back is important so you don’t strain your muscles or put undue pressure on your spine. By taking the necessary steps to reduce the negative effects of sitting, you can help protect your health and remain active and healthy.
Conclusion
Prolonged sitting can lead to serious health hazards, ranging from increased risk of obesity, diabetes, and heart disease, to increased stress and poor posture. Furthermore, sitting for extended periods can decrease overall physical activity, which can have ripple effects on a person’s physical and mental well-being. Fortunately, there is a way to minimize the effects of prolonged sitting by getting up, moving around at regular intervals, and engaging in regular exercise. Doing so can help to reduce the risks associated with sitting for too long and help to ensure that our bodies remain healthy and strong.